Published on March 21, 2023
Is it time to strike a new balance between state intervention and market forces?
Industrial policy is gaining momentum in many countries, with some economists pointing to China's model as a success. In a world facing challenges such as the COVID-19 aftermath, vaccine nationalism, global supply-chain instability, net zero transitions, and geopolitical competition, there is renewed debate about the role of industrial policy and government support for firms and industries deemed strategically important.
People are questioning whether we can trust the free market, and there are concerns that countries are losing their innovation edge. National security hawks also worry about relying on adversaries for critical resources such as semiconductors and pharmaceuticals.
In the US, industrial policy is no longer a taboo subject. There is bipartisan support for the Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors and Science Act (CHIPS Act), which aims to revitalize the US semiconductor industry. More than 90 percent of advanced chips, crucial for defense and artificial intelligence (AI), come from Taiwan Province of China—which raises concerns about US industry vulnerability in case of an attack. To address such risks, the US government is allocating $39 billion in funding from the $280 billion CHIPS Act to support the development of advanced semiconductor manufacturing capability. The Biden administration's industrial policy is far-reaching, and at least two semiconductor manufacturing clusters are planned by 2030. Funding recipients also face extensive conditions, such as a 10-year ban on expanding advanced chip capacity in China and a commitment to affordable childcare. These policies are part of the administration's broader approach to industrial policy, which also includes $370 billion in subsidies for clean energy in the Inflation Reduction Act.
Meanwhile, Japan is providing subsidies worth more than $500 million to 57 companies to encourage them to invest domestically—as part of its efforts to reduce reliance on China. Similarly, the European Union is scaling up its industrial policy—including by setting aside €160 billion of its COVID-19 recovery fund for digital innovations such as chips, batteries, and climate adaptation. In response to massive subsidies in the US Inflation Reduction Act, Italy's economy minister recently called for a common EU approach to support competitiveness and protect strategic production.
Focus on national champions
“Industrial policy” refers to government efforts to shape the economy by targeting specific industries, firms, or economic activities. This is achieved through a range of tools such as subsidies, tax incentives, infrastructure development, protective regulations, and research and development support.
When implementing industrial policy as part of their growth strategy, countries are often faced with competing objectives, such as securing sustainable economic growth, maintaining financial and fiscal stability, and establishing “national champions.”
Establishing national champions is often a distinct objective of a nation’s growth strategy. Several considerations underpin this objective, including: (i) enhancing national security by promoting self-sufficiency in key industries, (ii) supporting job-rich and inclusive growth, (iii) revitalizing left-behind communities, and (iv) the voter optics associated with reviving the manufacturing sector.
Various countries have promoted specific firms or industries as national champions—such as semiconductors in Taiwan Province of China, renewable energy in Germany, and aerospace in France. This approach aims to create globally competitive companies, ensuring economic growth and security.
Although the use of industrial policy to establish national champions has been successful in some cases, it remains controversial. Economists worry that picking winners and losers can lead to market distortions and inefficient allocation of resources. Despite the concerns, the revival of industrial policy shows no signs of slowing down.
In a world of increasing economic nationalism and geopolitical tensions, establishing national champions is likely to remain an important policy objective for governments seeking to advance their national interests. In this context, the Growth Strategy Trilemma framework I develop below can guide policymakers in striking a balance among economic growth, stability, and national champion objectives.
The Growth Strategy Trilemma
The framework highlights the challenges policymakers face in balancing the competing demands of economic growth, financial and fiscal stability, and the establishment of national champions. Pursuing any two of these objectives comes at the cost of partially sacrificing the third, making it a trilemma.
Chart 1 illustrates the Growth Strategy Trilemma with its three competing objectives. The trilemma presents a difficult choice for policymakers.
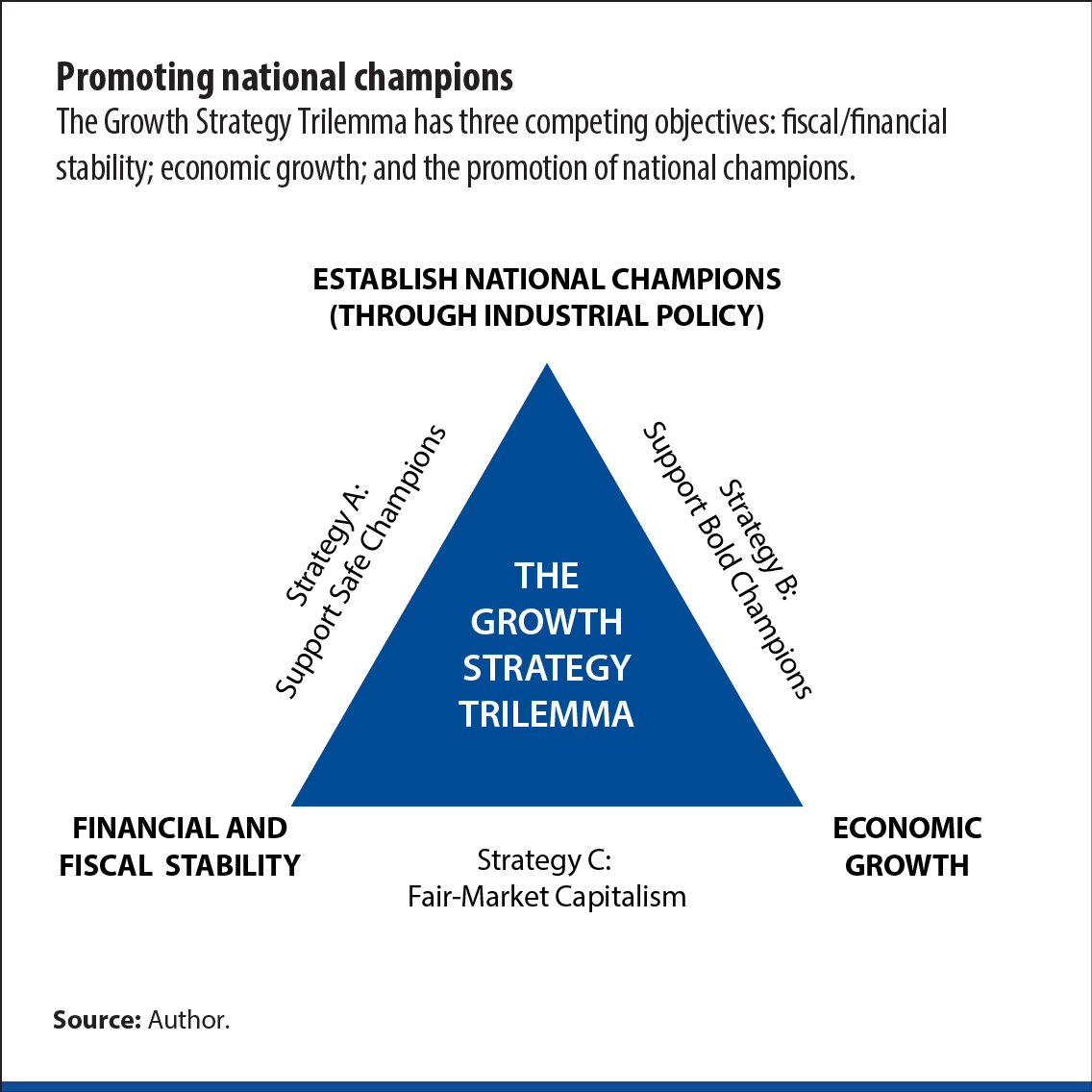
Governments that support safe champions (Strategy A) prioritize financial and fiscal stability along with support for safe national champions. This strategy often emphasizes national security, prudence, and resilience over the potential benefits of a more aggressive growth strategy.
The strategy of supporting bold champions (Strategy B) emphasizes economic growth and the selection of risk-taking national champions. However, this approach may result in less attention to stability concerns. This could result from greater risk-taking activity or less focus on efficiency and governance—leading to potential costs to the financial system and resulting in fiscal costs. Still, governments that pursue this strategy are willing to accept a higher risk of instability to pursue higher growth.
Finally, the fair-market capitalism approach (Strategy C) prioritizes stability along with economic growth—without a focus on national champions. Instead, the emphasis is on supporting a dynamic market economy along with free entry and ensuring that businesses operate in a fair and competitive marketplace.
Fair-market capitalism also offers a different path to achieving national security goals than the industrial policy approach. Instead of each country promoting national champions, the approach encourages a diversified global supply chain based on open and fair trade, thus avoiding an economic arms race. This approach can lead to greater efficiency and innovation in the long run while mitigating risks of supply-chain disruptions through diversification and international cooperation.
These trade-offs are not simply about choosing one objective over the other, but rather striking a balance among the three (on a continuum). The best approach for any government will depend on a range of contextual factors, including the state of the economy, the financial system's health, electoral pressures in the political system, and the geopolitical environment.
Nevertheless, efficiency gains may make it sensible to move toward the fair-market capitalism strategy. Yet governments often succumb to the temptation of establishing national champions. Why? A key factor could be the psychology of national leadership and the pressures on government leaders when choosing economic policies.
Why leaders embrace national champions
Imagine for a moment the life of a country leader. You have been elected to lead your country and are now responsible for decisions that will impact the well-being of millions of people. You must balance the competing demands of economic growth, national security, financial and fiscal stability, and social and environmental concerns. The stakes are high, and the pressure can be overwhelming.
A significant pressure you face as a country leader is the need to deliver economic growth. Achieving adequate growth can be essential for maintaining your political power, providing jobs, and ensuring the stability of your society. Without sustained growth, you may face mounting unemployment and social discontent, endangering your political tenure.
This pressure can manifest as growth anxiety. Clinical psychology studies show that anxiety causes people to become fixated on immediate concerns, often at the expense of long-term goals. In the context of economic growth, leaders may experience similar anxieties that cause them to prioritize short-term performance and quick wins to relieve their anxiety and demonstrate progress. This can lead to a narrow focus on particular industries or companies perceived as providing immediate growth—and disregard for the potential stability risks and downsides of this approach.
In this context, industrial policy is a key tool at your disposal. This can involve awarding contracts, providing subsidies or tax breaks, or investing in infrastructure projects to establish national champions. However, promoting national champions can also have negative consequences. It can result in a concentration of economic power, misallocation of resources, and neglect of long-term considerations. It can also undermine market competition and innovation, ultimately harming growth and social welfare.
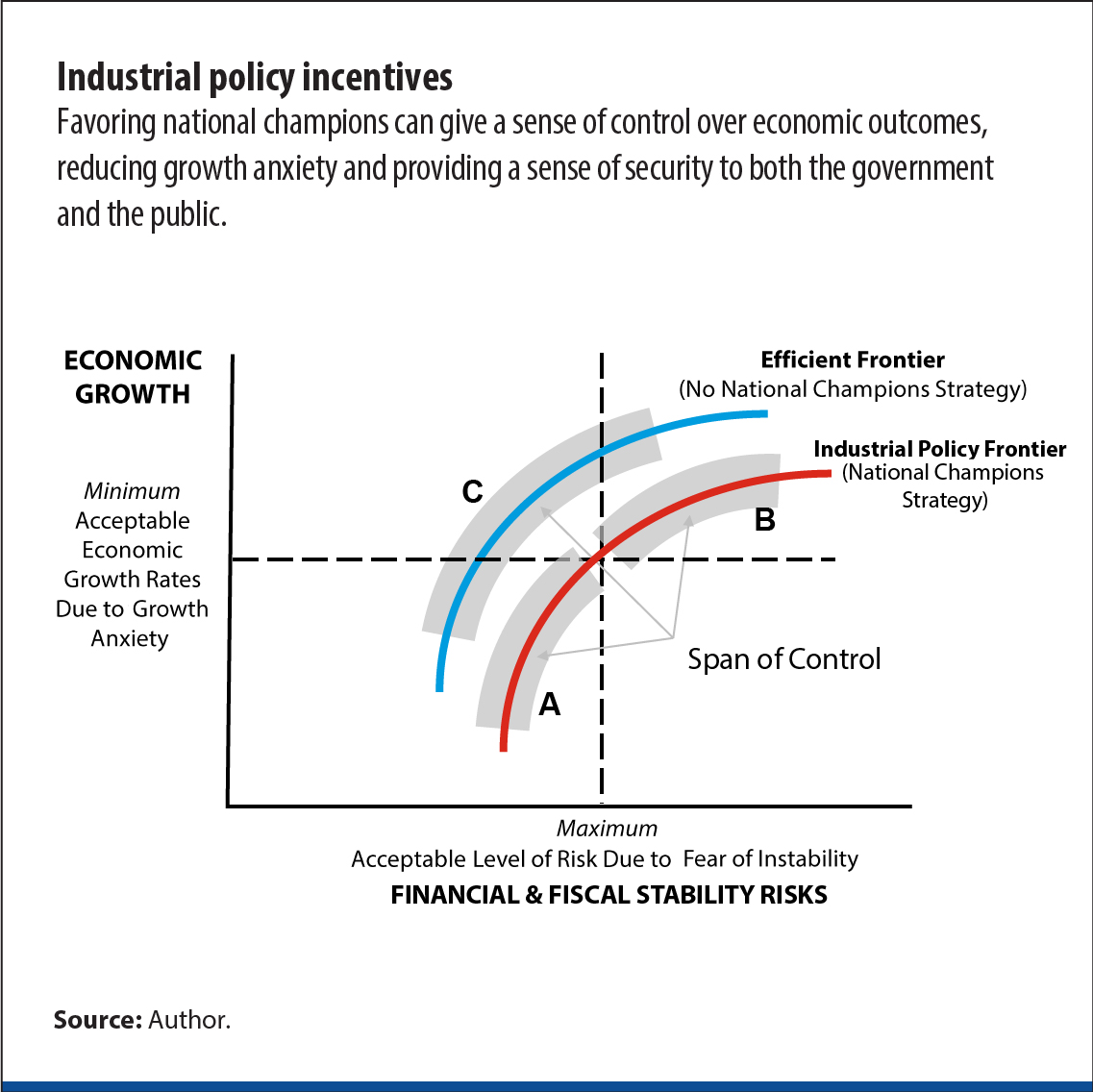
Despite these costs and inefficiencies, you may be compelled to promote bold champions (Strategy B). This is because you could be under intense pressure to deliver quick wins, maintain political power, or provide jobs for your citizens. Moreover, industrial policy can give a sense of control over economic outcomes, reducing growth anxiety and providing a sense of security to both the government and the public (Chart 2).
Separately, as a leader, you may face immense pressure to safeguard national security and maintain financial and fiscal stability. This pressure can trigger a fear of instability. The fear can be driven by concerns over national security—such as dependence on other countries for critical resources—or a desire to avoid major failures, defaults, or scandals.
When faced with such fears, you may be motivated to pursue a strategy that promotes safe national champions to achieve security and stability goals. You may see this as a way to protect the country's interests, secure critical resources, and maintain stability—which provides a sense of control over outcomes (Strategy A). However, it is essential to consider the potential downsides of this approach, such as the risk of distorting competition and hindering innovation.
Altogether, growth anxiety and fear of instability are strong motivators that can prompt country leaders to choose national champions. These political and psychological factors often shape a country's growth strategy, even though most leaders are aware of the potential long-term economic costs and inefficiencies.
Closing thoughts
The Airbus case is often hailed as a model of successful government intervention in the economy. The creation of the Airbus consortium in Europe in the late 1960s—which challenged the dominance of Boeing in world markets—was made possible through government subsidies, commitments to absorb losses, and financing for fixed development costs. As a result, Airbus became a formidable competitor.
However, the recent Chinese experience with the COMAC C919 aircraft shows that industrial policy is far from a silver bullet. Driven by the conviction that a great nation should have its own airliners, China has invested heavily in developing its commercial aircraft to challenge the dominance of Boeing and Airbus. Despite investing up to $70 billion in the Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China (COMAC), China's state-owned manufacturer, the project has been delayed by more than five years as a result of regulatory, technological, and supply-chain hurdles. The delays were compounded by the special licensing requirements for technology parts exports to China imposed by the Trump administration in 2020. The C919 also hasn’t been certified yet by any major aviation authority outside China, partly due to safety issues. Thus, despite industrial policy success with its domestic high-speed rail network during the 2010s, China has not been able to replicate this achievement in the competitive global aviation industry.
The lesson here is that promoting national champions can sometimes be effective, but it's not a guaranteed recipe for success. Even in other cases of market failure, the government may find it challenging to address the problem without causing significant distortions or incurring high fiscal costs. Furthermore, when several countries engage in industrial policy to promote their own national champions, it can lead to a race to the bottom in terms of subsidies and protections. Such dynamics reduce the chances of success for any individual country and can create an unstable global economic environment.
Former US Treasury Secretary Lawrence Summers recently said he liked his industrial policy advisers the same way he liked generals. “The best generals are the ones who hate war the most but are willing to fight when needed. What I worry is that people who do industrial policy love doing industrial policy.” In this context, the Trilemma reminds policymakers to take a cautious approach to industrial policy—while focusing on long-term growth, stability, and international cooperation.
Just like salt in cooking, a pinch of industrial policy can be helpful, but too much can overpower, and prolonged excess can harm.
Podcast

Industrial policy refers to a set of policies that governments use to bolster national industries or companies deemed strategically important for economic competitiveness, social outcomes, or national security. In this podcast, Agarwal says while the practice of choosing national champions fell out of favor in the 1980s, rising geopolitical tensions of late have sparked a renewed interest in industrial policy, which is often a guise for protectionism.
Opinions expressed in articles and other materials are those of the authors; they do not necessarily reflect IMF policy.









