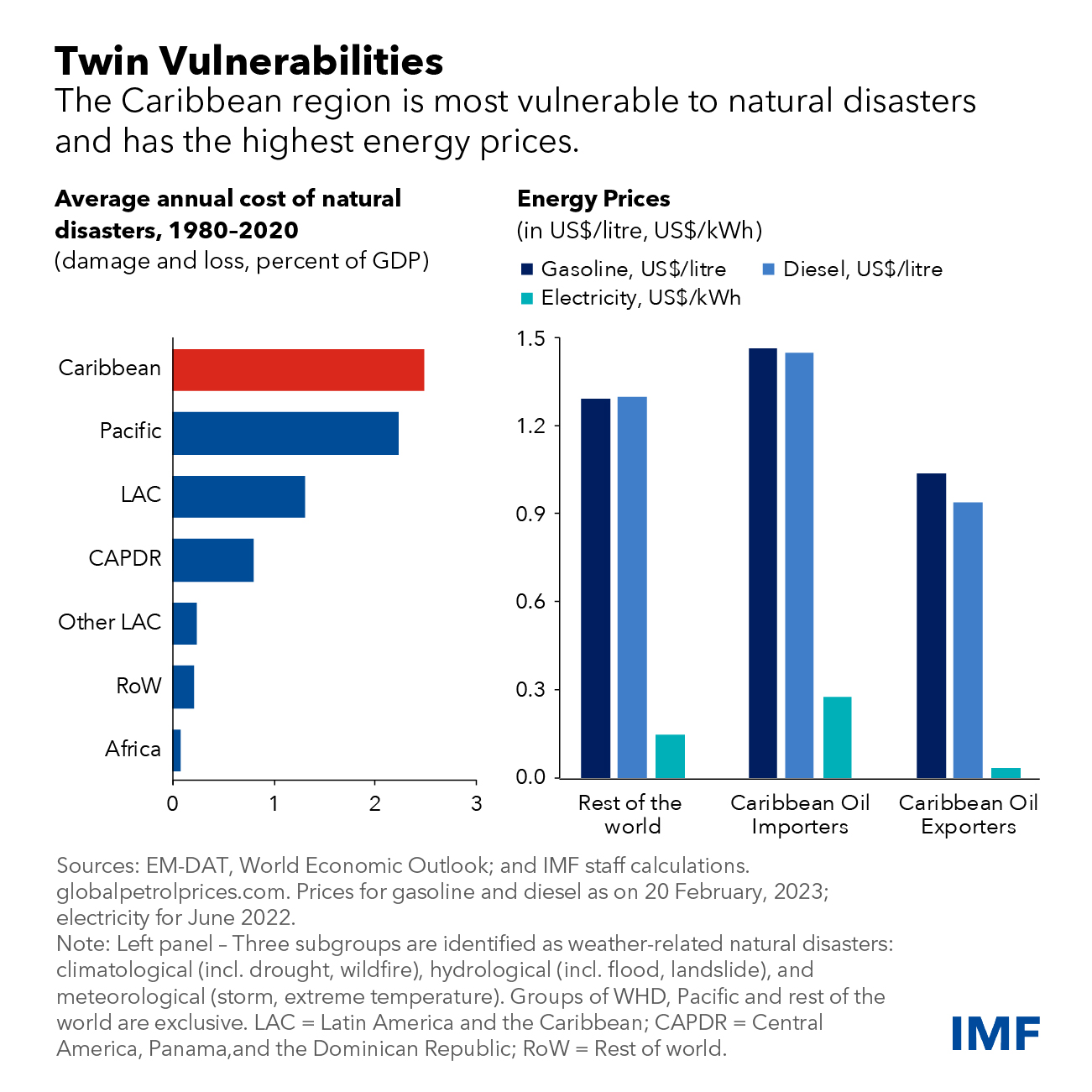
The Caribbean is the most exposed region to climate-related natural disasters, with estimated adaptation investment needs of more than $100 billion, equal to about one-third of its annual economic output.
Moreover, with electricity largely generated using fossil fuels, energy prices in the Caribbean are among the highest in the world, highlighting the need for investment in lower-cost and lower-carbon energy production.
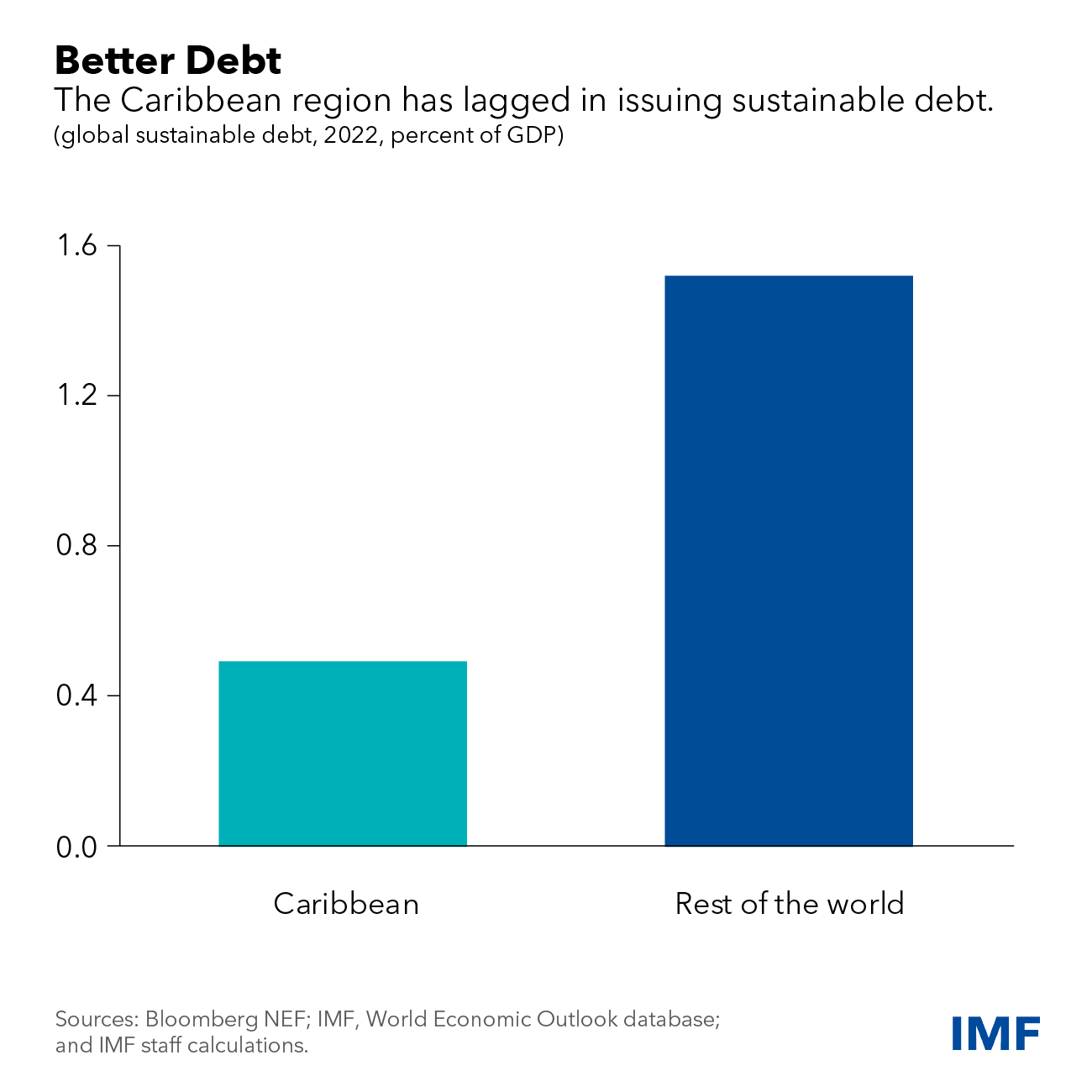
The current level of private climate finance in the Caribbean region falls well short of what is needed. Some recent initiatives are promising, including:
- Issuance of
blue bonds combined with
debt-nature swaps for debt service reduction opening fiscal space for nature conservation
investments in coastal areas (Belize and Barbados).
- Issuance of a catastrophe bond for financial protection against
hurricane damage (Jamaica).
- State-contingent debt instruments that provide debt service relief after natural disasters in the context of debt restructuring in IMF-supported programs (Barbados and Grenada).
However, Caribbean countries have only been approved for about $800 million from climate funds (Green Climate Fund, Global Environment Fund, and Adaptation Fund).
While most countries purchase disaster insurance from the
Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility, and a few countries are also enrolled in
World Bank contingency credit lines, coverage levels are below the needs for rehabilitation and
reconstruction.
Access to private climate financing has been low due to several factors.
A pipeline of bankable climate projects is critical for raising private financing, but this remains insufficient due to limited capacity and expertise for project preparation. Similarly, qualification requirements to access climate funds are often beyond the administrative capacity of small country and microstates’ governments, given the fixed costs of project evaluation and appraisal.
The multifaceted nature of climate finance operations, which include finance, legal, environmental and budget aspects, requires the involvement of several departments across the public administration leading to costly and lengthy preparation periods. Also, data gaps undermine project appraisal and monitoring, limiting risk pricing and impact evaluation. Also, private financing usually requires information about collateral and creditworthiness, which is often not readily available. Finally, a lack of effective carbon pricing reduces the incentive of investors to channel funds into climate-beneficial projects.
In many countries, the high level of government debt reduces the fiscal space for sharing risks (for example, government guarantees for private sector financing). This is particularly critical considering that climate investments are needed now while the return accrues in the long term. Also, the fixed costs of issuing financial instruments to raise money for climate adaptation constrain access to private financing.
Collaborative Solutions
Addressing these obstacles to private climate finance requires coordinated action by all those involved.
Governments need to strengthen the institutions and processes that develop, execute, and fund climate-related projects. These include green tagging of projects in budgets, accreditation to apply to climate finance, and upgrading procurement, transparency and reporting standards. To overcome constraints related to small size, Caribbean countries could pool administrative resources to reduce costs, while strengthening communication across departments involved in climate finance operations. Sustainable fiscal positions, supported by transparent and binding medium-term fiscal frameworks to signal commitment to debt sustainability, are critical to sustain access to climate finance at favorable terms.
Governments could also facilitate access to private sector finance with the modernization of foreclosure procedures and accounting and reporting standards, and the establishment of credit bureaus. Given that social benefits will be larger than private benefits, governments should also remove bottlenecks at the sectoral level by adopting clear legal and regulatory environments for renewable energy and eliminating fossil fuel subsidies, especially those for electricity production.
Financial markets that supply climate finance can simplify application processes, qualification requirements, and financial instruments, without weakening standards. Some options include establishing frameworks to pool applications of several countries and projects, making application requirements proportional to the amounts being requested. Climate finance instruments can be standardized to reduce appraisal cost and potentially facilitate the development of secondary markets for climate instruments.
The IMF and other international financial institutions can give advice to help countries maintain fiscal sustainability and provide climate-specific technical assistance to develop administrative capacity, and climate data and diagnostic tools. The IMF also provides long-term concessional climate financing to strengthen the enabling environment, institutions and implementation capacity to address climate challenges and helps support private climate financing with the Resilience and Sustainability Facility. Multilateral development banks could play a role in helping Caribbean countries with high levels of government debt to leverage equity financing from private sources.